Cisco Meraki vMX SD-WAN with AWS Cloud WAN Deployment
This lab guide covers deploying Cisco Meraki vMX SD-WAN appliances on AWS with AWS Cloud WAN to connect on-premises branches with AWS workloads using BGP connectivity.
Overview
This guide covers deploying the Cisco Meraki vMX Partner Solution with AWS Cloud WAN in the AWS Cloud.
The Cisco Meraki vMX is deployed in AWS Cloud WAN to enable customers to easily connect their on-premises branches to their AWS workloads through BGP-based routing.
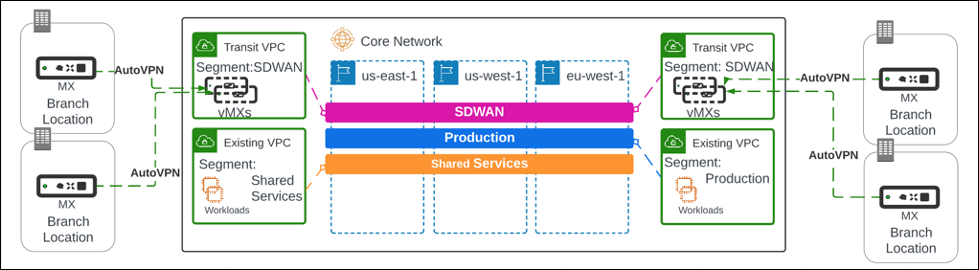
Meraki vMX is a virtualized security and SD-WAN network appliance. This Cloud WAN deployment includes vMX as a node to extend the common policy, segmentation, and security of SD-WAN environments at scale. The deployment includes an active-active (or active-standby) pair of redundant vMX appliances in a highly available configuration. With AWS Cloud WAN, connectivity can be scaled across virtual private clouds (VPCs) with workloads in multiple AWS Regions. You can configure, monitor, and maintain all of your Meraki devices from a single Meraki dashboard.
Architecture: Cloud WAN with BGP Connectivity
This automation builds the regional vMXs that interconnect your on-premises branches to a new or existing Cloud WAN network. It uses BGP to manage end-to-end routing as well as failover in case of vMX failure.
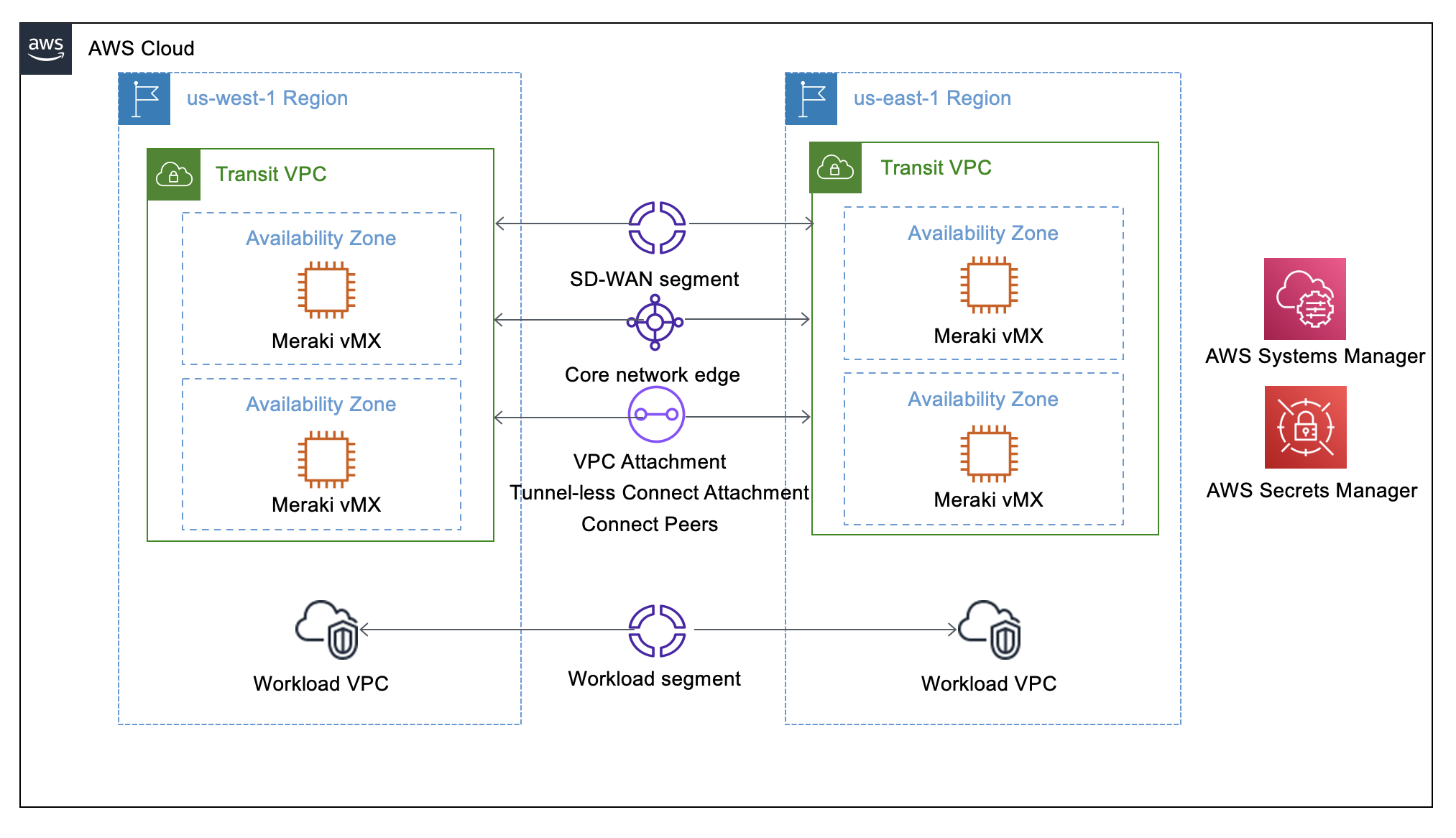
This deployment sets up the following:
- Highly available Transit VPC (TVPC) that can be created in multiple AWS Regions
- Each TVPC can be connected to an existing Cloud WAN(CW) network. If no CW network is available, a new CW network can be created via the CloudFormation template
- Two Availability Zones in each VPC that contain a vMX appliance with internet access via an internet gateway
- AWS Cloud WAN Global Network (if new CW network is created) that includes:
- A core network with a core network policy that includes the routing policy
- A software-defined wide area networks (SD-WAN) segment that can be integrated into customer-provided workload segments
- Routes from each vMX branch connected via the transit VPCs are propagated throughout the SD-WAN segment for sharing with additional workload segments
- VPC Attachment, Tunnel-less Connect(TLC) Attachment, and a TLC Connect Peer for each vMX deployed
- For each Region deployed, an AWS Cloud WAN core network edge for connecting workload VPCs to the transit VPC
- AWS Secrets Manager to store a vMX API key, which is used by AWS Lambda to access the Meraki dashboard when updating route tables
- AWS Systems Manager Parameter Store to store vMX tag values used for CloudFormation automation
Prerequisites
Before deploying this solution, ensure you have the following:
AWS Account Configuration
- Sign in to your AWS account with an IAM user role that has the necessary permissions
- Make sure that your AWS account is configured correctly with appropriate service limits and permissions
Meraki Dashboard Account Preparation
- Enable API access to your Meraki organization. For more information, see Cisco Meraki Dashboard API
- Add vMX licenses to the Meraki dashboard. For more information, see Add Another License
Meraki Dashboard Configuration
As long as you have available vMX licenses (small, medium, or large), and an API Key, the CloudFormation template will create the licensed Meraki vMX network and provide each vMX with a name and tag that is used for automation.
Deployment Options
Deploy vMX with Cloud WAN into a new VPC
This option builds a new AWS environment that consists of the VPC, subnets, security groups, Cloud WAN Core Network, Attachments and other infrastructure components. It also launches Meraki vMX networks in the Meraki Dashboard.
Post-Deployment Configuration
After deployment, you must complete the following steps:
Verify Meraki vMX Networks
Two Meraki vMX networks have been created each with a generated name and tag: <AWS TVPC-vMX-REGION-vMX#-AZ#-ACCOUNT>
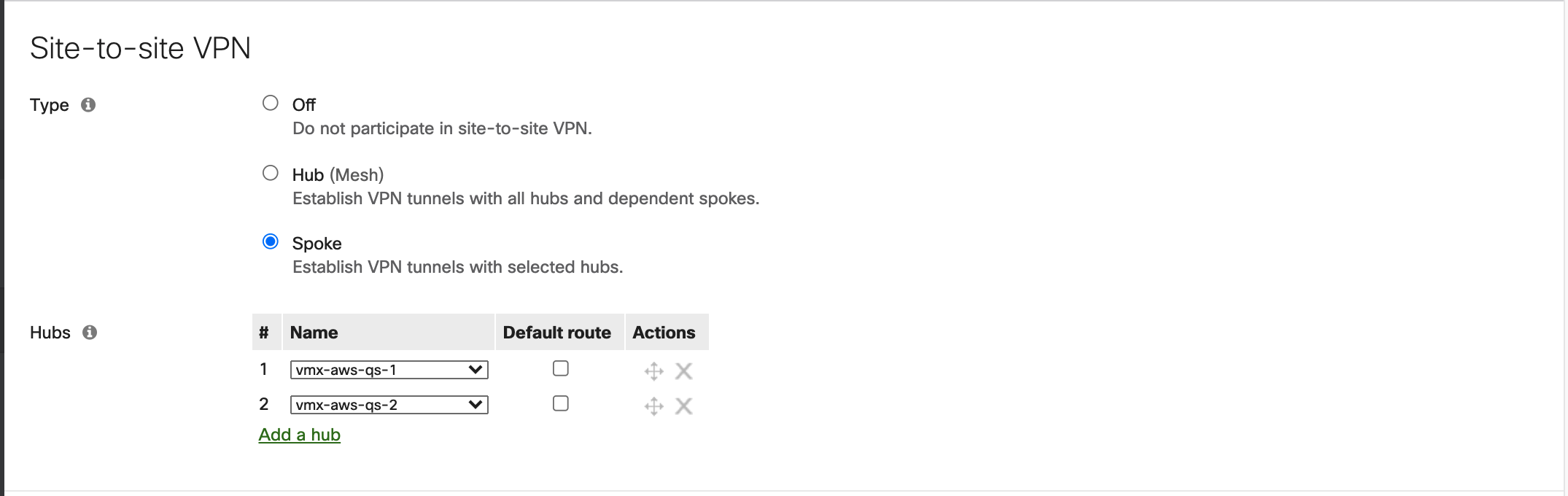
Configure Meraki Spokes
- Configure your branch sites as Meraki Auto VPN spokes with the vMX instances as the primary and secondary hubs. For more information, see Meraki Auto VPN - Configuration and Troubleshooting
- From each branch network, advertise the local subnet into autoVPN
Configure BGP
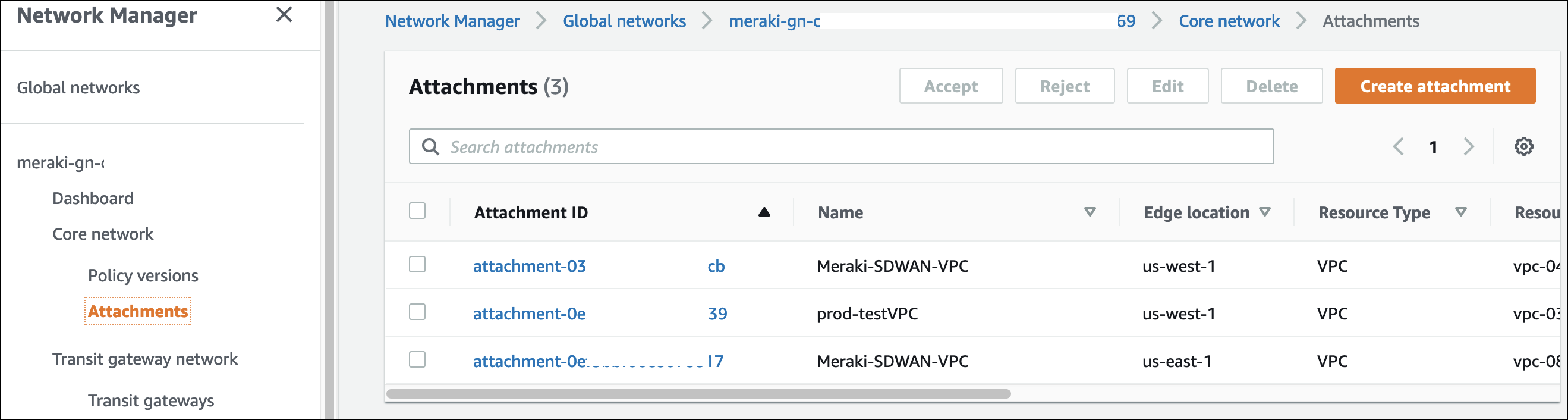
- Navigate to Network Manager > Global Network > Attachments > Connect Attachment > Connect Peers
- Identify the two Inside CIDR addresses associated with each peer as well as the ASN number for the region
- Note the subnet identifies if the neighbors will peer with the Active vMX (vMX-0) or the standby (vMX-1)
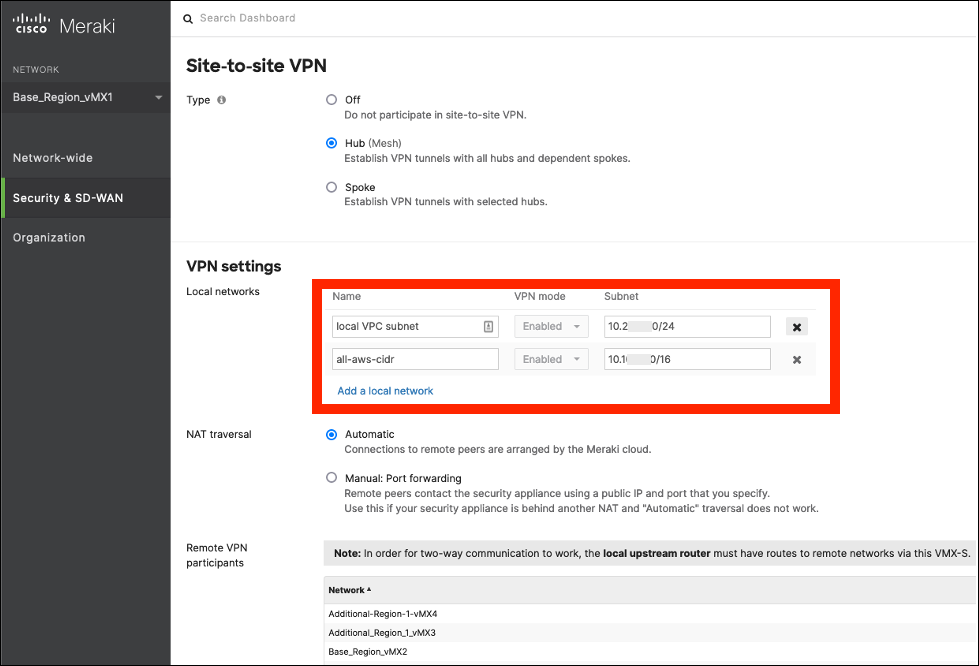
- Navigate to each Meraki vMX network's BGP page at network
<AWS TVPC-vMX-REGION-vMX#-AZ#-ACCOUNT>> Security & SD-WAN > Routing - Enable BGP with your BGP ASN and the two neighbor relations that correspond with the active and standby vMX routers
vMX High Availability Architecture
The deployment architecture is fault tolerant with two vMX instances in different Availability Zones. BGP routing provides automatic failover capabilities when a vMX instance fails.
Testing vMX Failover
Failover can be tested by using a network ACL in the subnet of the active vMX that denies all traffic. Both AutoVPN and BGP protocol will detect an outage. Remove the ACL to test fail back.
BGP Failover Process: BGP, based upon the hold down timer values, will detect an outage and use AS Path to communicate that the standby vMX is now primary.
Best Practices
For best practices when using Meraki vMX on AWS, see vMX Setup Guide for Amazon Web Services (AWS).
Additional Architecture Diagrams
Cloud WAN Core Network
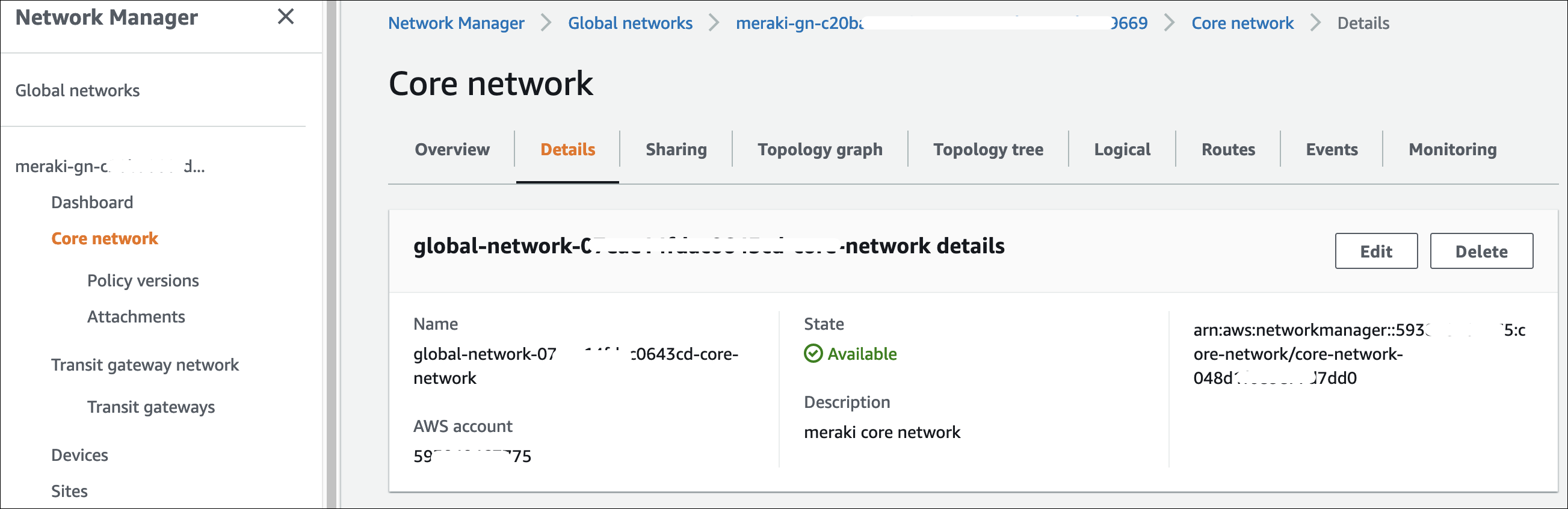
Cloud WAN Global Network
Cloud WAN Overview
This completes the Cisco Meraki vMX SD-WAN deployment with AWS Cloud WAN. The solution provides highly available, scalable connectivity between your on-premises branches and AWS workloads through BGP-based routing in the Cloud WAN architecture.