Cisco Meraki vMX SD-WAN with AWS Transit Gateway Deployment
This lab guide covers deploying Cisco Meraki vMX SD-WAN appliances on AWS with AWS Transit Gateway to connect on-premises branches with AWS workloads using Lambda-based failover automation.
Overview
This guide covers deploying the Cisco Meraki vMX Partner Solution with AWS Transit Gateway in the AWS Cloud.
The Cisco Meraki vMX is deployed with AWS Transit Gateway to enable customers to easily connect their on-premises branches to their AWS workloads through automated route management.
Meraki vMX is a virtualized security and SD-WAN network appliance. This Transit Gateway deployment includes vMX as a node to extend the common policy, segmentation, and security of SD-WAN environments at scale. The deployment includes an active-active (or active-standby) pair of redundant vMX appliances in a highly available configuration. With AWS Transit Gateway, connectivity can be scaled across virtual private clouds (VPCs) with workloads in multiple AWS Regions. You can configure, monitor, and maintain all of your Meraki devices from a single Meraki dashboard.
Architecture: Transit Gateway Connectivity
This automation builds the regional vMXs that interconnect your on-premises branches to a new or existing Transit Gateway network. It uses AWS Lambda to run a 1 or 10 minute polling function that detects failover scenarios.
High Availability Architecture Options
The solution supports flexible deployment architectures:
Single HA Pair Deployment
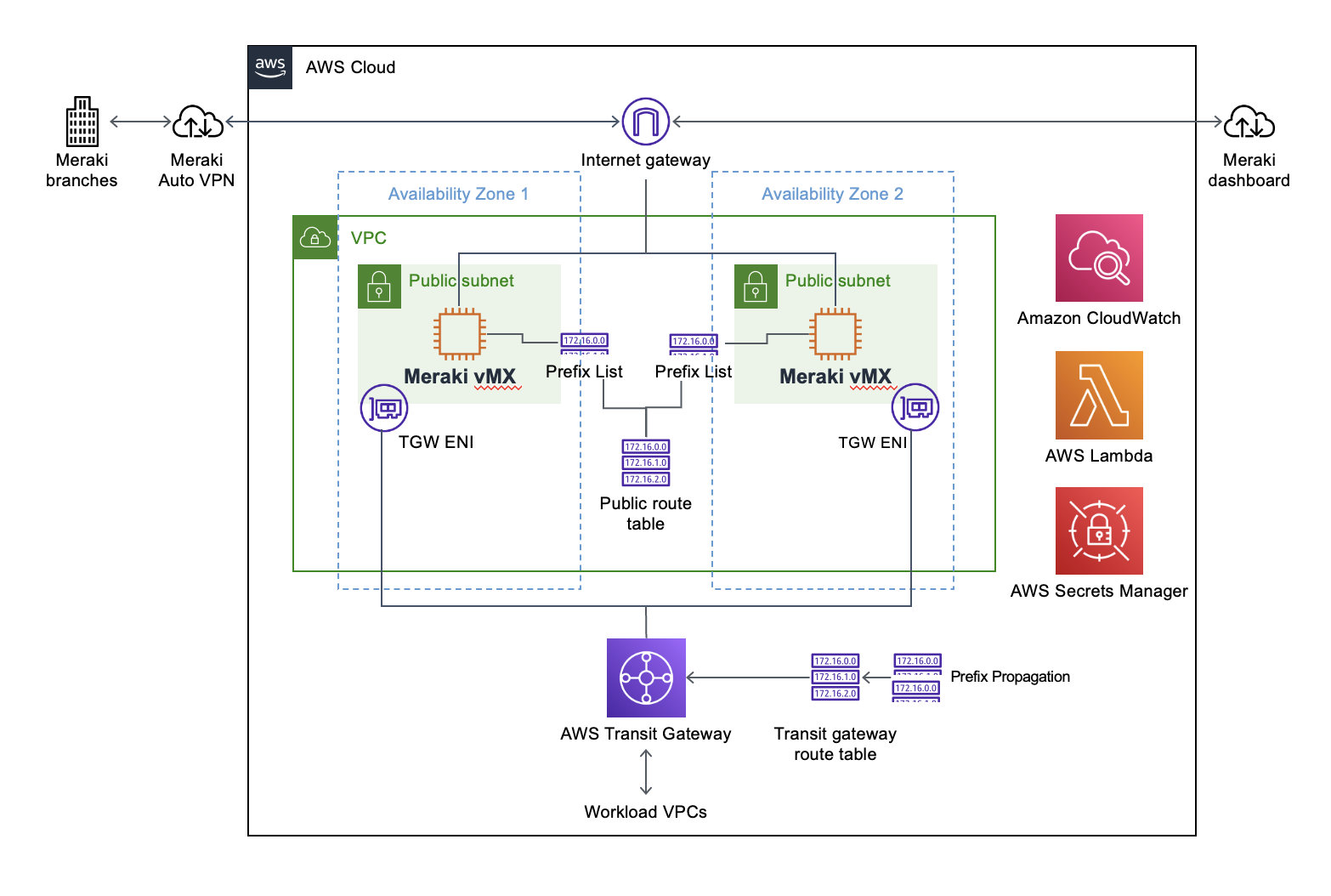
A single highly available pair with one vMX in each Availability Zone (2 vMXs total). This provides basic redundancy for branch connectivity.
Dual HA Pair Deployment
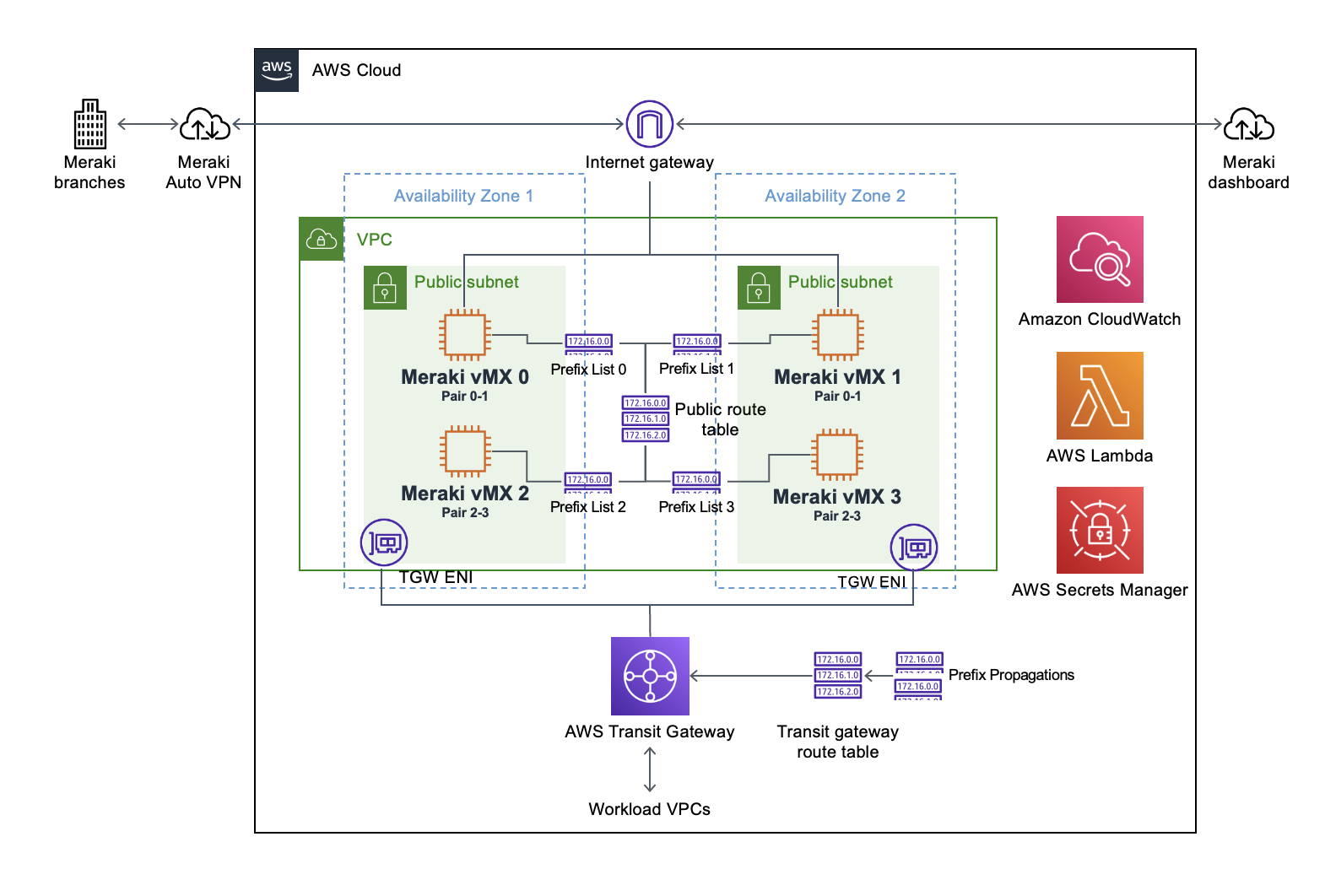
Two highly available pairs with 2 vMXs per Availability Zone (4 vMXs total). Each pair consists of one vMX in each AZ. This architecture supports: - Higher throughput requirements - Traffic segmentation between different branch groups - Additional redundancy and load distribution
Automated Failover Scenario
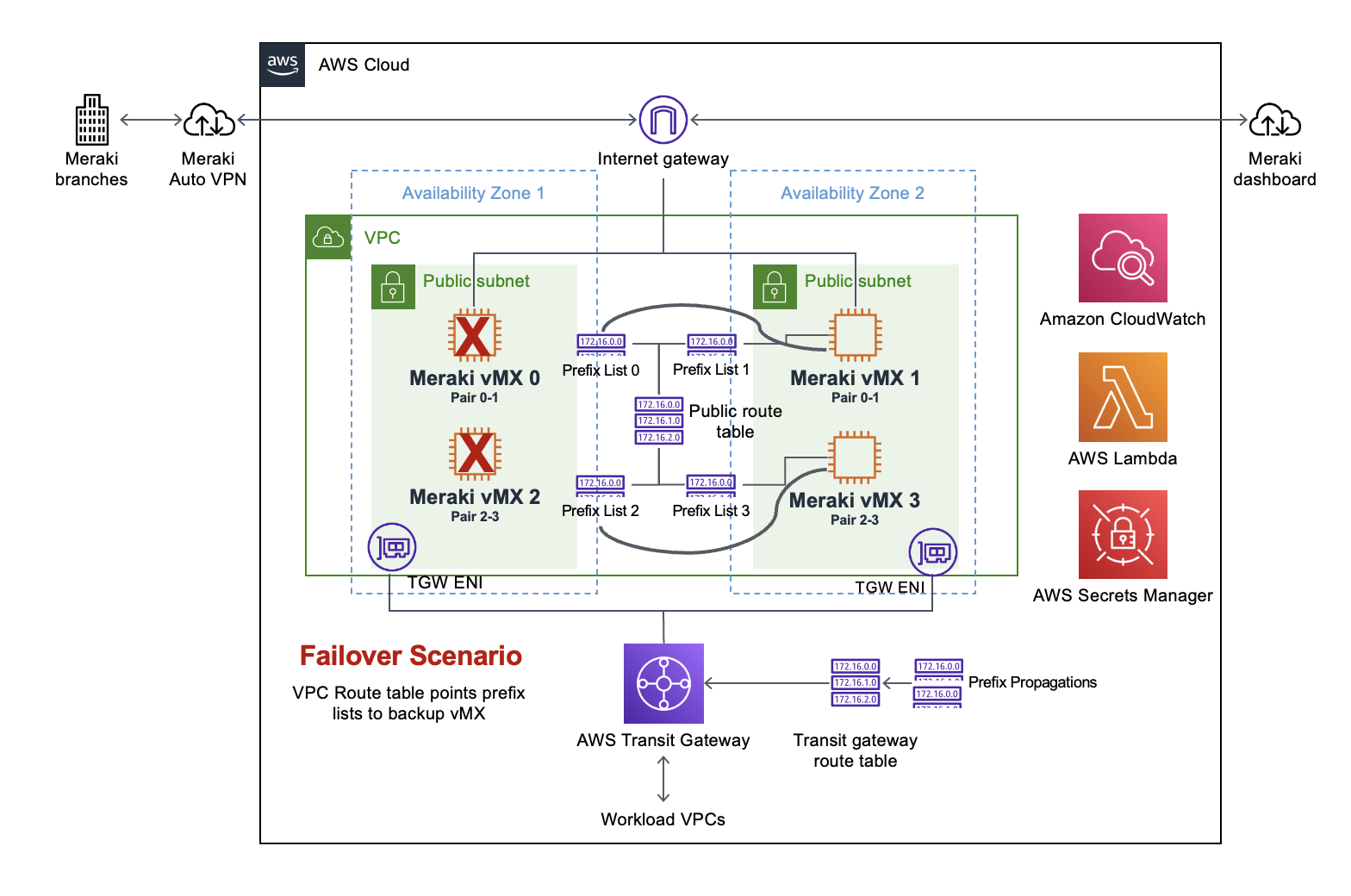
When an Availability Zone becomes unavailable or a vMX fails, the Lambda function automatically updates routing: - VPC route table entries pointing to the failed vMX's prefix list are redirected to the backup vMX in the healthy AZ - Traffic seamlessly fails over to the surviving vMX instances - The process reverses automatically when the failed components recover
Lambda Polling Function: How It Works
The Lambda function provides intelligent monitoring and automated failover using AWS Managed Prefix Lists for efficient route management. This approach offers significant advantages over managing individual routes:
Key Efficiency Improvements: - Scalability: A single prefix list can contain up to 1,000 CIDR blocks, eliminating the need to manage hundreds of individual route table entries - Atomic Updates: Changes to prefix lists propagate automatically to all associated route tables without individual route modifications - Reduced API Calls: One prefix list update replaces potentially hundreds of individual route creation/deletion operations - Simplified Failover: During failover, only the next-hop needs updating for the entire prefix list, rather than modifying each route individually
Lambda Operation Modes
Auto Route Learning Mode
The Lambda function automatically discovers and manages routes from your Meraki SD-WAN environment:
- Route Discovery: Calls the Meraki Dashboard API (
getOrganizationApplianceVpnStatuses) to identify all spoke branches in the AutoVPN network - Intelligent Summarization: Automatically summarizes spoke CIDRs using IP address collapsing to minimize prefix list entries
- Prefix List Management:
- Creates managed prefix lists named
pl-<vMX-Tag>for each vMX in an HA pair - Dynamically updates prefix lists when spokes are added or removed
- Automatically adjusts prefix list size (MaxEntries) based on the number of routes
- Route Table Updates: Injects prefix list references into both VPC and Transit Gateway route tables
- Automatic Failover: Monitors vMX health and redirects prefix list routes to standby vMX upon failure
Manual Route Mode
Provides automated failover while allowing manual control of route summarization:
- Manual Route Definition: Add summarized routes manually to the VPC route table pointing to prefix lists
- Manual TGW Configuration: Manually add Transit Gateway route table entries for prefix lists
- Automatic Failover: Lambda monitors vMX health and updates prefix list next-hops to standby vMX upon failure
- Simplified Management: Useful when you want to control route summarization or have specific routing requirements
Lambda Function Architecture
The polling function executes on a CloudWatch Events schedule (1 or 10 minutes) and performs the following workflow:
1. Health Monitoring
For each vMX in every HA pair: - Queries AWS EC2 instance status to verify the instance is running - Queries Meraki Dashboard API to verify the vMX reports "online" status - Considers vMX healthy only when both checks pass
2. Route Learning (Auto Mode Only)
For each HA pair:
├─ Query Meraki Dashboard for all spoke networks
├─ Filter spokes that peer with this vMX pair
├─ Extract exported subnets from each spoke
├─ Summarize routes using IP address collapsing
└─ Generate separate prefix lists for vMX1 and vMX2 based on hub priority
3. Prefix List Management
The function intelligently manages AWS Managed Prefix Lists:
- Creates prefix lists on first run with naming convention pl-<vMX-Tag>
- Updates prefix lists when routes change (max 100 changes per API call)
- Optimizes MaxEntries size based on current route count
- Waits for prefix list state to reach "complete" before proceeding
4. Route Table Updates
VPC Route Table:
If both vMXs online:
├─ pl-vMX1 → vMX1 instance
└─ pl-vMX2 → vMX2 instance
If vMX1 online, vMX2 offline:
├─ pl-vMX1 → vMX1 instance
└─ pl-vMX2 → vMX1 instance (failover)
If vMX1 offline, vMX2 online:
├─ pl-vMX1 → vMX2 instance (failover)
└─ pl-vMX2 → vMX2 instance
Transit Gateway Route Table: - Prefix lists always point to the TGW VPC attachment - TGW handles routing to the appropriate vMX based on VPC routes
5. Multi-Pair Support
The Lambda function supports multiple HA pairs through a tag-based JSON structure:
{
"pair-0": ["vMX0-tag", "vMX1-tag"],
"pair-1": ["vMX2-tag", "vMX3-tag"]
}
Each pair is processed independently with separate prefix lists and failover logic.
Performance Characteristics
Efficiency Gains with Prefix Lists: - Before (Individual Routes): Managing 100 spoke branches = 100 VPC route entries + 100 TGW route entries = 200 API calls per update - After (Prefix Lists): Managing 100 spoke branches = 2 prefix lists (1 per vMX) + 2 route table entries = ~10-20 API calls per update - Failover Speed: Individual routes require sequential updates; prefix lists enable instant failover by changing a single next-hop
Polling Function Execution: - Typical execution time: 30-45 seconds for single HA pair - Memory allocation: 3008 MB for optimal performance - Timeout: 60 seconds
This deployment sets up the following:
- Highly available architecture that spans two Availability Zones
- VPC configured with public and private subnets, according to AWS best practices, to provide you with your own virtual network on AWS
- Internet gateway that connects the VPC to the internet
- VPC route table associated with the public subnets to specify routing rules for outbound internet traffic
- Meraki vMX appliances in the public subnets on Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) instances
- Elastic network interfaces in the private subnets to enable traffic routing from all subnets in the Availability Zone to AWS Transit Gateway
- AWS Transit Gateway attached to the VPC, enabling connectivity to attached workload VPCs in other AWS Regions
- Transit gateway route table associated with the VPC for routing rules to AWS Transit Gateway
- Amazon CloudWatch to collect logs of vMX instance performance
- AWS Lambda to monitor the state of the vMX instances. If an instance fails, AWS Lambda updates route tables to point to a healthy instance and logs the event in CloudWatch
- AWS Secrets Manager to store a Meraki API key. AWS Lambda uses the API key to access the Meraki dashboard when updating route tables
Prerequisites
Before deploying this solution, ensure you have the following:
AWS Account Configuration
- Sign in to your AWS account with an IAM user role that has the necessary permissions
- Make sure that your AWS account is configured correctly with appropriate service limits and permissions
Meraki Dashboard Account Preparation
- Enable API access to your Meraki organization. For more information, see Cisco Meraki Dashboard API
- Add vMX licenses to the Meraki dashboard. For more information, see Add Another License
Meraki Dashboard Configuration
As long as you have available vMX licenses (small, medium, or large), and an API Key, the CloudFormation template will create the licensed Meraki vMX network and provide each vMX with a name and tag that is used for automation.
Deployment Options
Deploy vMX with Transit Gateway into a new VPC
This option builds a new AWS environment that consists of the VPC, subnets, security groups, Transit Gateway, TGW Route Table, and other infrastructure components. It also launches Meraki vMX networks in the Meraki Dashboard.
Post-Deployment Configuration
After deployment, you must complete the following steps:
Verify Meraki vMX Networks
Two Meraki vMX networks have been created each with a generated name and tag: <AWS TVPC-vMX-REGION-vMX#-AZ#-ACCOUNT>
Configure Meraki Spokes
- Configure your branch sites as Meraki Auto VPN spokes with the vMX instances as the primary and secondary hubs. For more information, see Meraki Auto VPN - Configuration and Troubleshooting
- From each branch network, advertise the local subnet into autoVPN
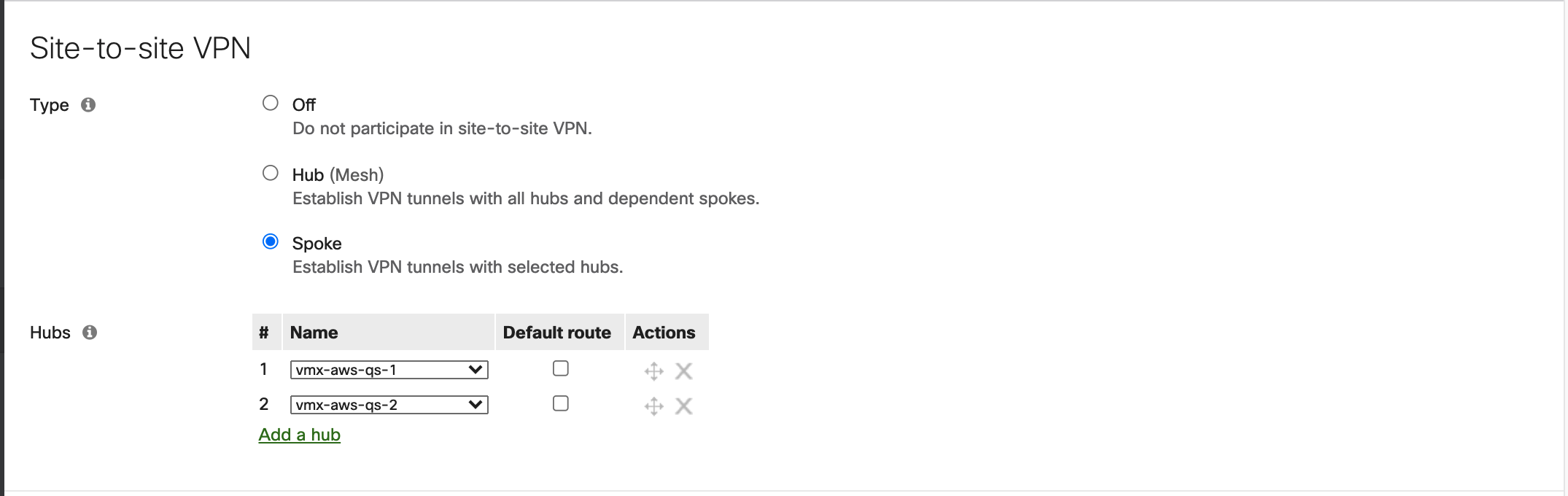
Configure Transit Gateway Integration
- Attach workload VPCs to the transit gateway. For more information, see Transit gateway attachments to a VPC
- Update the VPC route table for the workload subnets. For more information, see Add and remove routes from a route table
Auto Route Learning Mode Configuration
In Auto mode, the Lambda function automatically discovers spokes and manages prefix lists. Verify the automation is working:
1. Check Prefix Lists
Navigate to VPC Console → Managed Prefix Lists to see the auto-created lists:
- pl-<vMX1-Tag>: Contains routes for spokes using vMX1 as primary hub
- pl-<vMX2-Tag>: Contains routes for spokes using vMX2 as primary hub
2. Verify VPC Route Table
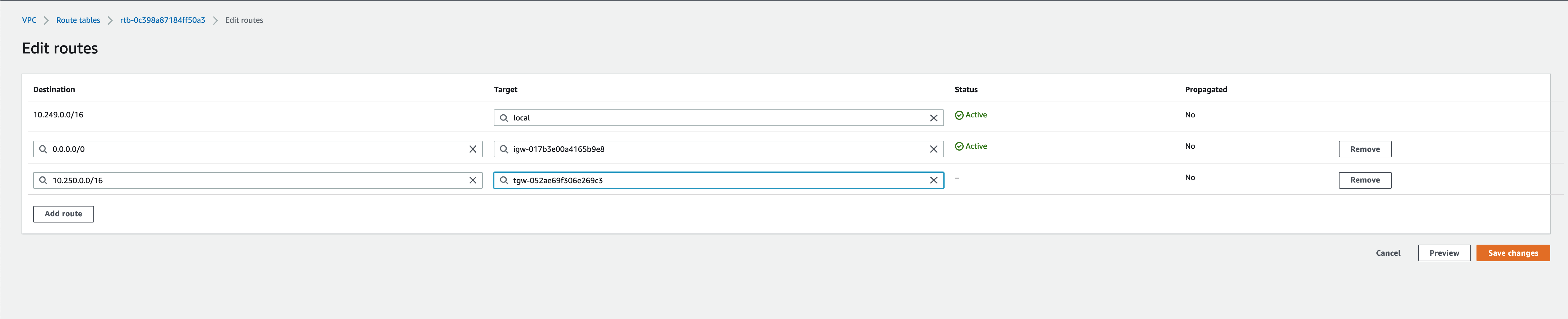
The VPC route table should contain prefix list references:
- Destination: pl-<vMX1-Tag> → Target: vMX1 instance ID
- Destination: pl-<vMX2-Tag> → Target: vMX2 instance ID
3. Verify Transit Gateway Route Table
TGW route table should contain prefix list references pointing to the VPC attachment:
- Destination: pl-<vMX1-Tag> → Attachment: TGW VPC Attachment
- Destination: pl-<vMX2-Tag> → Attachment: TGW VPC Attachment
4. Add New Spoke Branches
When you add new spoke branches to the Meraki AutoVPN network: 1. Configure the spoke with vMX1 and vMX2 as hubs 2. Advertise local subnets from the spoke 3. Wait for the next Lambda execution (1-10 minutes) 4. Verify the spoke's routes appear in the appropriate prefix list
The Lambda function automatically: - Learns new routes from the Meraki Dashboard API - Summarizes CIDRs for efficiency - Updates prefix lists with new spoke routes - Maintains route tables without manual intervention - Handles failover by updating prefix list next-hops
Manual Route Mode Configuration
In Manual mode, you control route summarization while the Lambda handles failover automation.
1. Create Prefix Lists Manually
Create managed prefix lists for each vMX:
- Navigate to VPC Console → Managed Prefix Lists → Create prefix list
- Name: pl-<vMX1-Tag> and pl-<vMX2-Tag>
- Add your summarized CIDR blocks
2. Add VPC Route Table Entries
Add routes to the VPC route table:
- Destination: pl-<vMX1-Tag> → Target: vMX1 instance (primary)
- Destination: pl-<vMX2-Tag> → Target: vMX2 instance (primary)
Important: Point routes to the primary vMX initially. Lambda will handle failover automatically.
3. Add TGW Route Table Entries
Manually add Transit Gateway route table entries:
- Destination: pl-<vMX1-Tag> → Attachment: VPC Attachment
- Destination: pl-<vMX2-Tag> → Attachment: VPC Attachment
4. Update Prefix Lists as Needed
When branch networks change, manually update the prefix list entries to reflect new routes.
The Lambda function will: - Monitor vMX health continuously - Automatically failover by updating prefix list next-hops to the standby vMX - Restore routes when the primary vMX recovers - Not modify prefix list entries (you maintain full control)
vMX High Availability Architecture
The deployment architecture is fault tolerant with two vMX instances in different Availability Zones. An AWS Lambda function handles instance-level failures by checking the state of vMX EC2 instances. For software-level failures, it checks the vMX health state on the Meraki dashboard. In the case of a vMX instance failure, the AWS Lambda function logs the error in CloudWatch and updates the VPC and transit gateway routes to point to a healthy instance.
Testing vMX Failover
You can test the automated failover functionality to verify the Lambda function correctly handles failures.
Test Method 1: Network ACL (Recommended)
- Identify the subnet containing the primary vMX (typically vMX in AZ1)
- Create a Network ACL that denies all inbound and outbound traffic
- Associate the NACL with the vMX subnet
- Wait for the Lambda polling interval (1-10 minutes)
- Verify failover occurred by checking:
- VPC route table shows prefix lists now point to the secondary vMX
- CloudWatch logs show Lambda detected the failure
- Branch connectivity remains active through secondary vMX
- Remove the restrictive NACL to test fail-back
- Wait for the next polling interval
- Verify routes restore to the original primary vMX
Test Method 2: Stop EC2 Instance
- Stop the primary vMX EC2 instance
- Wait for Lambda polling interval
- Verify prefix list routes failover to secondary vMX
- Start the instance to test fail-back
Lambda Failover Process with Prefix Lists
The Lambda polling function (running every 1 or 10 minutes) executes this workflow during failover:
Detection Phase:
For each HA pair:
├─ Check vMX1 EC2 instance status
├─ Check vMX1 Meraki Dashboard status
├─ Check vMX2 EC2 instance status
└─ Check vMX2 Meraki Dashboard status
Failover Phase (if vMX1 fails):
VPC Route Table Updates:
├─ pl-vMX1 → Change next-hop from vMX1 to vMX2 (1 API call)
└─ pl-vMX2 → Keep next-hop at vMX2 (no change)
Result: All routes in both prefix lists now flow through vMX2
Key Advantages: - Speed: Only 1-2 route table modifications needed regardless of spoke count - Atomicity: All routes in the prefix list failover simultaneously - Reliability: No risk of partial failover leaving some routes unreachable - Visibility: CloudWatch logs clearly show which prefix lists failed over
Expected CloudWatch Log Output:
vMX Status: vMX-TVPC-us-east-1-vMX0-1a online and vMX-TVPC-us-east-1-vMX1-1b offline, moving all routes to vMX-TVPC-us-east-1-vMX0-1a
AWS VPC RT: Updating vpc route table rtb-xxxxx, setting i-xxxxx as next hop for prefix list pl-xxxxx
AWS VPC RT: Updating vpc route table rtb-xxxxx, setting i-xxxxx as next hop for prefix list pl-yyyyy
Fail-back Behavior:
When the failed vMX recovers: 1. Lambda detects both vMXs are online 2. Routes automatically restore to original configuration 3. pl-vMX1 points back to vMX1 4. pl-vMX2 points back to vMX2 5. Traffic redistributes across both vMXs
Monitoring and Troubleshooting
CloudWatch Logs
The Lambda function logs all activities to CloudWatch Logs. To view logs:
- Navigate to CloudWatch → Log Groups
- Find log group:
/aws/lambda/vMX-Update-Lambda-<TagPrefix> - View log streams for each execution
Key Log Messages:
# Successful Health Check
vMX Status: <vMX1-Tag> and <vMX2-Tag> are both online
# Route Learning (Auto Mode)
AutoVPN summarized routes with <vMX-Tag> as primary: ['10.0.0.0/8', '172.16.0.0/12']
# Prefix List Updates
AWS PL: Updating prefix list pl-xxxxx
AWS PL: add cidr 192.168.1.0/24
AWS PL: Update complete for prefix list pl-xxxxx
# VPC Route Table Updates
AWS VPC RT: Updating vpc route table rtb-xxxxx, setting i-xxxxx as next hop for prefix list pl-xxxxx
# TGW Route Table Updates
AWS TGW RT: Updating transit gateway route table tgw-rtb-xxxxx, setting tgw-attach-xxxxx as next hop for prefix list pl-xxxxx
# Failover Events
vMX Status: <vMX2-Tag> online and <vMX1-Tag> offline, moving all routes to <vMX2-Tag>
Common Issues and Solutions
Issue: Prefix Lists Not Created
- Symptom: No prefix lists appear in VPC console after deployment
- Cause: Lambda hasn't executed yet or failed on first run
- Solution: Check CloudWatch logs for errors; verify Lambda has proper IAM permissions
Issue: Routes Not Updating
- Symptom: Prefix lists exist but VPC routes don't update
- Cause: Prefix list may be in "modify-in-progress" state
- Solution: Lambda waits for "complete" state; check if previous modification is stuck
Issue: Failover Not Occurring
- Symptom: vMX fails but routes don't update
- Cause: Lambda may not have access to Meraki API key or EC2 describe permissions
- Solution: Verify Secrets Manager contains valid API key; check Lambda IAM role
Issue: Both vMXs Show Offline
- Symptom: Lambda logs show both vMXs offline
- Action: Check EC2 instance states and Meraki Dashboard connectivity status
- Alert: Consider setting up CloudWatch alarms for this condition
Performance Tuning
Lambda Polling Interval Selection:
- 1-minute polling (rate(1 minute)):
- Faster failover detection (~1 minute)
- Higher Lambda invocation costs
-
Recommended for production environments requiring minimal downtime
-
10-minute polling (rate(10 minutes)):
- Slower failover detection (~10 minutes)
- Lower Lambda costs
- Suitable for dev/test environments or cost-sensitive deployments
Prefix List Sizing:
The Lambda automatically manages prefix list MaxEntries:
- Starts with minimum size (1 entry)
- Grows when routes are added
- Shrinks after routes are removed
- Maximum 1,000 entries per prefix list
Multi-Pair Scaling:
Each HA pair adds approximately 15-20 seconds to Lambda execution time: - Single pair: ~30-45 seconds - Dual pair: ~50-65 seconds - Ensure Lambda timeout (60s) accommodates your deployment size
Best Practices
Security
- API Key Protection: Meraki API key is stored in AWS Secrets Manager and never logged
- IAM Least Privilege: Lambda IAM role has only necessary permissions for EC2, VPC, TGW, and Secrets Manager
- Network Segmentation: Use separate HA pairs for different security zones or branch groups
Operational
- CloudWatch Alarms: Set up alarms for Lambda errors and both-vMXs-offline conditions
- Route Summarization: In Auto mode, the Lambda automatically summarizes routes for efficiency
- Tag Management: Use consistent tagging for vMX instances and networks to ensure proper Lambda operation
- Testing: Regularly test failover scenarios in non-production hours
Cost Optimization
- Polling Interval: Use 10-minute intervals for non-critical environments
- Prefix Lists: Prefix list approach significantly reduces costs compared to individual route management
- Right-Sizing: Deploy only the number of HA pairs needed for your throughput requirements
High Availability
- Multi-AZ: Always deploy vMX pairs across two Availability Zones
- Instance Type: Choose vMX size (small/medium/large) based on aggregate branch bandwidth
- Monitoring: Implement comprehensive monitoring of both AWS and Meraki components
For additional best practices when using Meraki vMX on AWS, see vMX Setup Guide for Amazon Web Services (AWS).
This completes the Cisco Meraki vMX SD-WAN deployment with AWS Transit Gateway. The solution provides highly available, scalable connectivity between your on-premises branches and AWS workloads through Lambda-automated prefix list management and failover capabilities. The prefix list approach delivers significant efficiency improvements over traditional individual route management, enabling faster failover, reduced API calls, and support for large-scale branch deployments.